Basics of Thermal Printing: How It Works & When to Use It.
Posted by Midwest Barcoding Solutions on Feb 17th 2025
Thermal printing is a popular printing technology used across various industries for tasks such as labeling, ticketing, barcode printing, and receipt generation. Unlike traditional inkjet or laser printers, thermal printers use heat to create images on specially treated paper or transfer ink from a ribbon onto a surface. This unique mechanism makes thermal printing an efficient, cost-effective, and reliable method, especially for high-volume printing needs.
This article explores how thermal printing works, its types, and its advantages over other printing methods, while also providing insight into when to choose direct thermal printing versus thermal transfer printing. We’ll also highlight the leading manufacturers of thermal printers and discuss key considerations for determining whether thermal printing is the right choice for your business or personal needs.

What is Thermal Printing?
Thermal printing is a digital printing process that produces images through controlled heat application rather than using ink or toner. It involves two primary methods: direct thermal printing and thermal transfer printing.
Compared to other printing technologies, thermal printing offers several advantages, including lower maintenance, faster printing speeds, and reduced long-term costs since it does not require ink cartridges or toners. These benefits make thermal printing a preferred choice for businesses that require high-speed and durable printing solutions.
How is Thermal Printing Different from Inkjet and Laser Printing?
|
Thermal printing differs significantly from inkjet and laser printing in its operational mechanism, materials used, and overall efficiency: |
||
|
Inkjet Printing: |
Laser Printing: |
Thermal Printing: |
While inkjet and laser printers are best suited for detailed, colorful, or office document printing, thermal printing excels in applications requiring speed, durability, and long-term cost efficiency.
Direct Thermal Printing vs. Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal printing is categorized into two main types: direct thermal and thermal transfer printing. While both use heat to create prints, they operate differently and are suited for different applications.
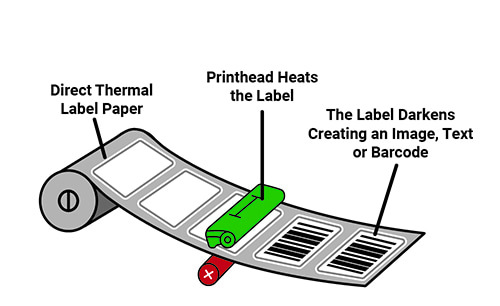
Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing involves applying heat directly to heat-sensitive paper, which darkens in response to heat exposure. This method does not require ink, toner, or ribbons, making it cost-effective and simple to operate.
|
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Common Uses:
|
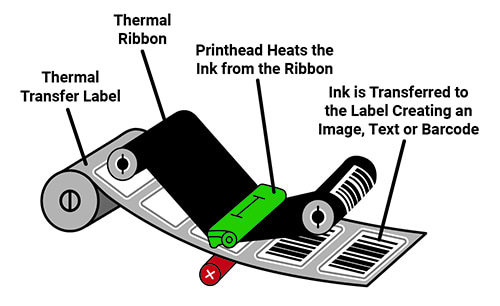
Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing uses a heated printhead to transfer ink from a ribbon onto a surface such as paper, plastic, or fabric. This process allows for more durable, high-quality prints that are resistant to heat, moisture, and
|
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Common Uses:
|
When to Choose Thermal Transfer Over Direct Thermal, and Vice Versa
Deciding between thermal transfer and direct thermal printing depends on several factors, including durability requirements, cost considerations, and intended applications.
|
Choose Direct Thermal If:
|
Choose Thermal Transfer If:
|
Leading Manufacturers of Thermal Printers
Several manufacturers specialize in producing high-quality thermal printers. Some of the industry leaders include:
|
Zebra Technologies Epson Brother |
Honeywell SATO TSC |
Questions to Ask Before Choosing a Thermal Printer
If you are unsure whether thermal printing is right for you, consider the following questions:
|
What is the primary purpose of my printing needs? How long do I need the prints to last? What materials will I be printing on? |
Do I need color printing? What is my budget for ongoing maintenance? Will my labels be exposed to harsh environments? |
Final Thoughts
Thermal printing is an efficient and cost-effective solution for businesses that require high-speed and durable printing. Understanding the differences between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing will help you choose the right method for your needs. While direct thermal is great for short-term applications, thermal transfer is the better option for long-lasting and durable prints.
By considering your specific requirements and assessing the advantages of each type of thermal printing, you can determine whether this technology aligns with your operational needs. If you’re in retail, logistics, healthcare, or manufacturing, thermal printing could be an ideal choice for optimizing your printing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Talk to an Expert
